OpenAI Agents SDK: Concepts, Workflow, Setup, and Why It Beats LangGraph
The OpenAI Agents SDK is designed to make building AI agents simple, fast, and production-ready. Instead of manually managing complex workflows, graphs, and routing logic, the SDK lets developers focus on what the agent should do, while OpenAI handles how it runs internally.
OpenAI Agents SDK
This article explains what the OpenAI Agents SDK is, why it exists, how it works, and how you can use it to build real-world AI agents.
1. What Is OpenAI Agents SDK?
The OpenAI Agents SDK is an official framework by OpenAI that helps developers build autonomous, intelligent AI agents that can think, decide, and act on their own.
It is designed to move beyond simple chatbots and enable real AI agents that can:
- Understand user intent
- Decide whether to answer directly or use tools
- Call APIs automatically
- Hand off tasks to other agents
- Stream responses in real time
- Maintain memory and context across sessions
The OpenAI Agents SDK focuses on high-level abstraction, meaning developers describe what the agent should do, not how every step should be executed.
Instead of manually managing workflows, retries, routing logic, or execution graphs, the SDK handles orchestration internally.
The OpenAI Agents SDK is a high-level framework that enables developers to build autonomous, tool-using, production-ready AI agents without manually controlling every workflow step.
2. Why Use OpenAI Agents SDK Instead of LangGraph?
When we build AI agents, the real challenge is not how smart the model is, but how the workflow is controlled. As systems grow bigger, controlling the flow becomes more important than just generating answers. This is where the difference between LangGraph and OpenAI Agents SDK becomes very clear.
How LangGraph Handles Workflows?
LangGraph works on the idea of a directed graph. This means the workflow moves step by step from one node to another in a fixed order. Every step must be clearly defined by the developer before the agent runs.
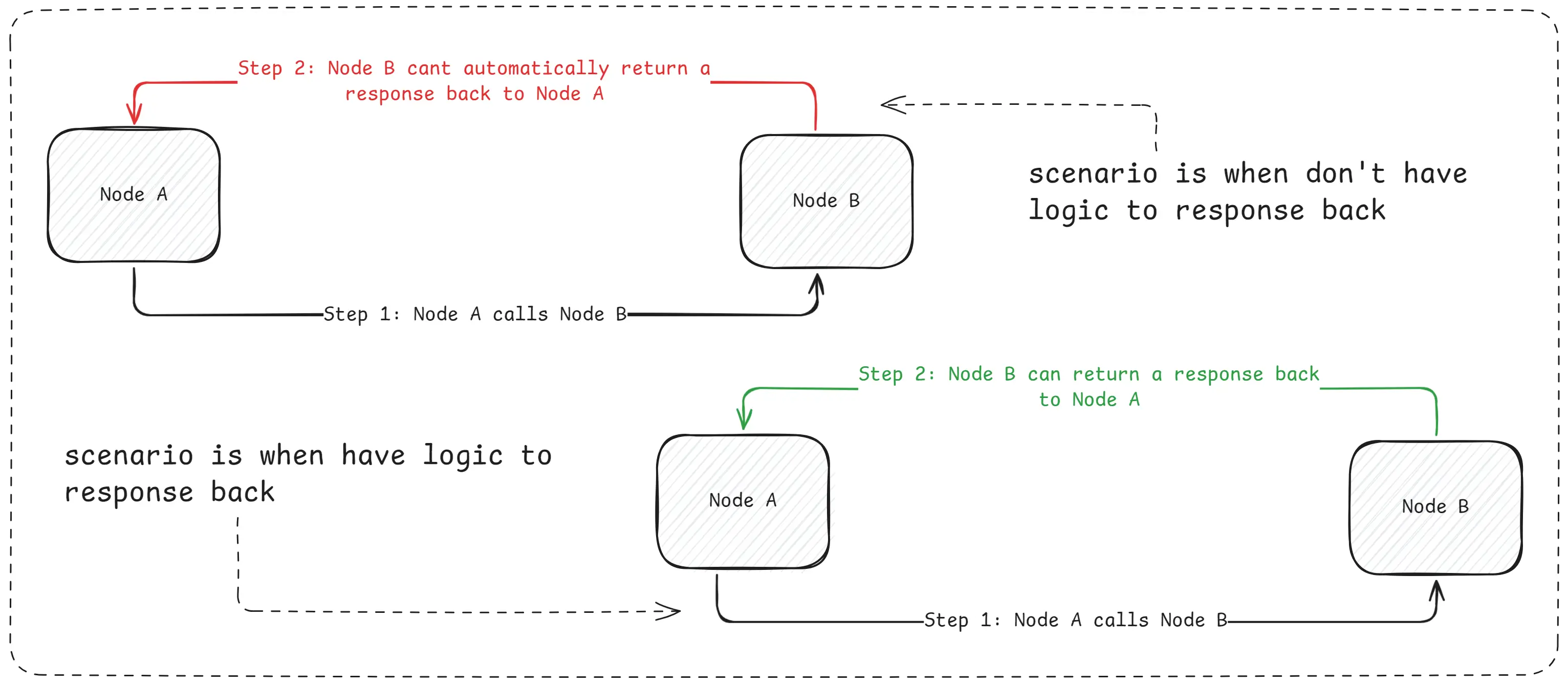
Scenario With LangGraph
In LangGraph, nothing happens automatically. If one node calls another node, the second node does not send a response back by itself. The developer must explicitly write code to return the response and decide where the flow goes next. If that logic is missing, the workflow simply stops.
Because of this, LangGraph behaves like a procedural system. It follows instructions exactly as written, just like a script. The system does not make decisions on its own. The developer controls every movement of data and every transition between nodes.
Real-World Limitation of LangGraph
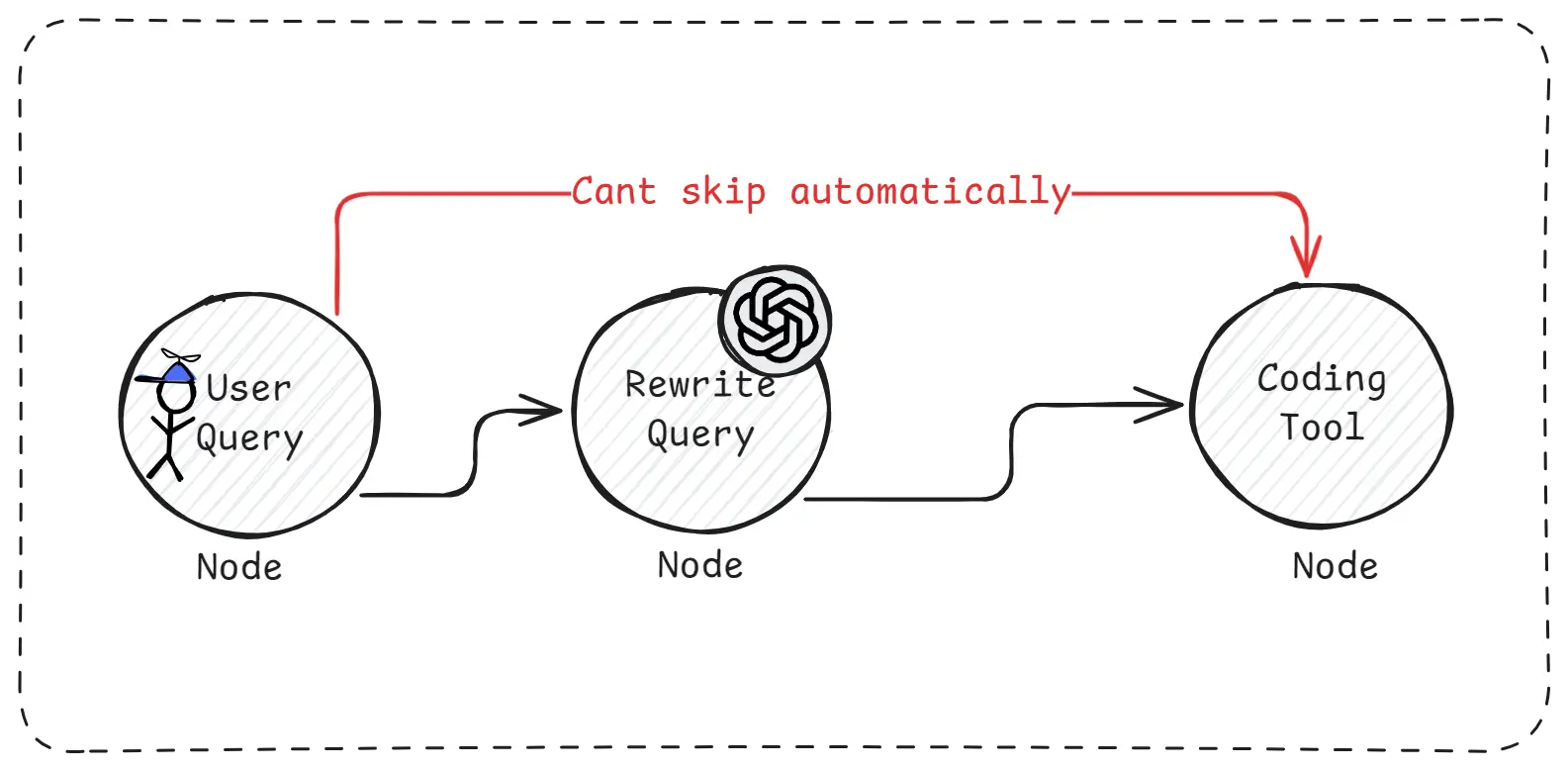
Real-World Limitation of LangGraph
Imagine a situation where the user asks a very clear and perfect question. Ideally, unnecessary steps like “Rewrite Query” should be skipped. However, LangGraph does not skip steps by default. Even if rewriting is not needed, the rewrite node will still execute unless the developer manually adds conditions to stop it.
This makes workflows longer and more complex. As more conditions and exceptions are added, the code becomes harder to read, harder to debug, and harder to scale. This is why LangGraph is described as non-autonomous and procedure-driven.
How OpenAI Agents SDK Works Differently?
OpenAI Agents SDK takes a more natural and flexible approach. Instead of controlling every step, you define the role of the agent, the tools it can use, and the rules it must follow. After that, the agent decides what to do next.
When one part of the agent uses another capability, the result flows back automatically. The agent understands whether it should continue, call another tool, or stop. There is no need to manually wire return paths or routing logic for every step.
Because of this, the system feels more like a thinking assistant rather than a fixed workflow.
Same Example With OpenAI Agents SDK
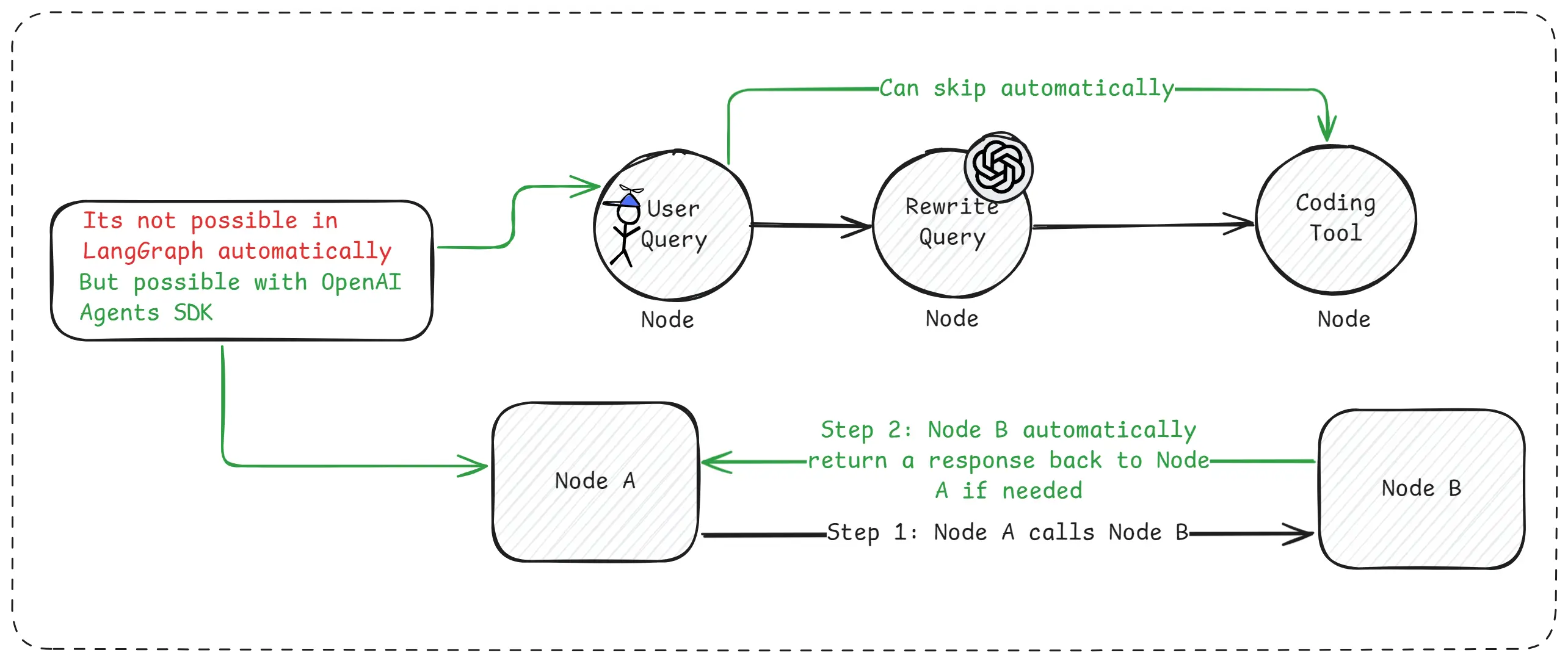
Same Example With OpenAI Agents SDK
In the same scenario where the user asks a perfect question, the agent immediately understands that rewriting is unnecessary. It skips that step on its own and directly calls the required tool. The final answer is returned without extra logic or manual routing.
This makes development faster and workflows much cleaner.
Simple Way to Understand the Difference
LangGraph works like a manual machine. Every step must be operated by the developer. If you forget to connect one part, the system breaks.
OpenAI Agents SDK works like an automatic system. You set the goal and rules, and the agent figures out the steps by itself.
Why OpenAI Agents SDK Feels Better in Practice?
OpenAI Agents SDK already includes tool calling, automatic result handling, streaming responses, human-in-the-loop support, tracing, and session management. All these features work together without requiring complex workflow wiring.
This makes it easier to build real-world AI agents that are reliable, flexible, and production-ready.
When LangGraph Still Makes Sense?
LangGraph is still useful when you need strict control and predictable execution. If every step must run in a fixed order and autonomy is not allowed, LangGraph provides that safety.
3. How Does OpenAI Agents SDK Work?
OpenAI Agents SDK works by letting agents manage the workflow themselves, instead of forcing developers to control every step manually.
The idea is simple, you define what the agent is, what tools it can use, and what task it should solve and after that, the agent handles the flow automatically.
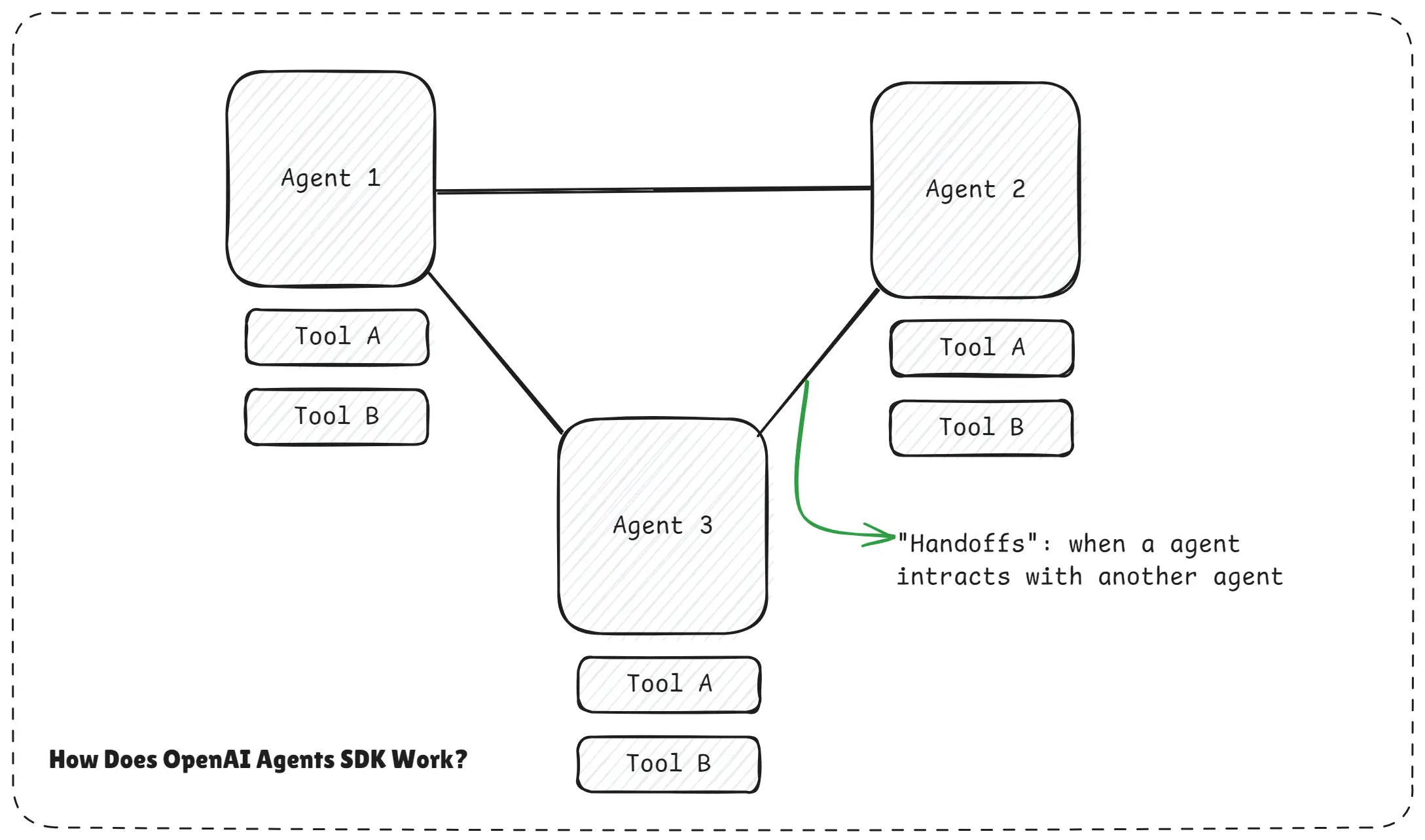
How Does OpenAI Agents SDK Work.webp
The diagram shows multiple agents connected through the OpenAI Agents SDK. Each agent has access to tools, but the SDK sits in the middle and coordinates everything.
When one agent interacts with another, this interaction is called a handoff. The important part is that no agent is hard-wired to a fixed path. The SDK allows smooth communication and automatic decision-making.
Step 1: You Create Specialized Agents
As a developer, you create agents for specific purposes.
For example, one agent may be good at searching, another at coding, and another at summarizing or planning.
Each agent is also connected to its own set of tools.
These tools could be APIs, databases, calculators, or any external service.
At this stage, you are only defining capabilities, not the execution order.
Step 2: Agents SDK Manages the Flow Automatically
Once the agents are defined, the OpenAI Agents SDK takes over the orchestration.
The SDK automatically:
- Decides which agent should act next
- Decides when a tool should be used
- Passes results between agents
- Decides when the task is complete
This means you do not need to manually define edges, return paths, or routing logic like in LangGraph. Agents can also handoff work to other agents when needed. If one agent realizes another agent is better suited for a task, it can transfer control smoothly.
Step 3: Agents Make Decisions on Their Own
Each agent independently decides:
- Where to go next
- How deep to explore a problem
- When to stop
You don’t need to manually define every possible path. The system adapts dynamically based on the task and context. This makes the workflow non-linear, flexible, and much closer to how humans actually work.
Simple Bank Analogy - Very Important to Understand OpenAI Agents SDK
Think of LangGraph like going to a bank where you must visit counters in a fixed order.
At every counter, you are told exactly where to go next. If the instructions are missing, you get stuck.
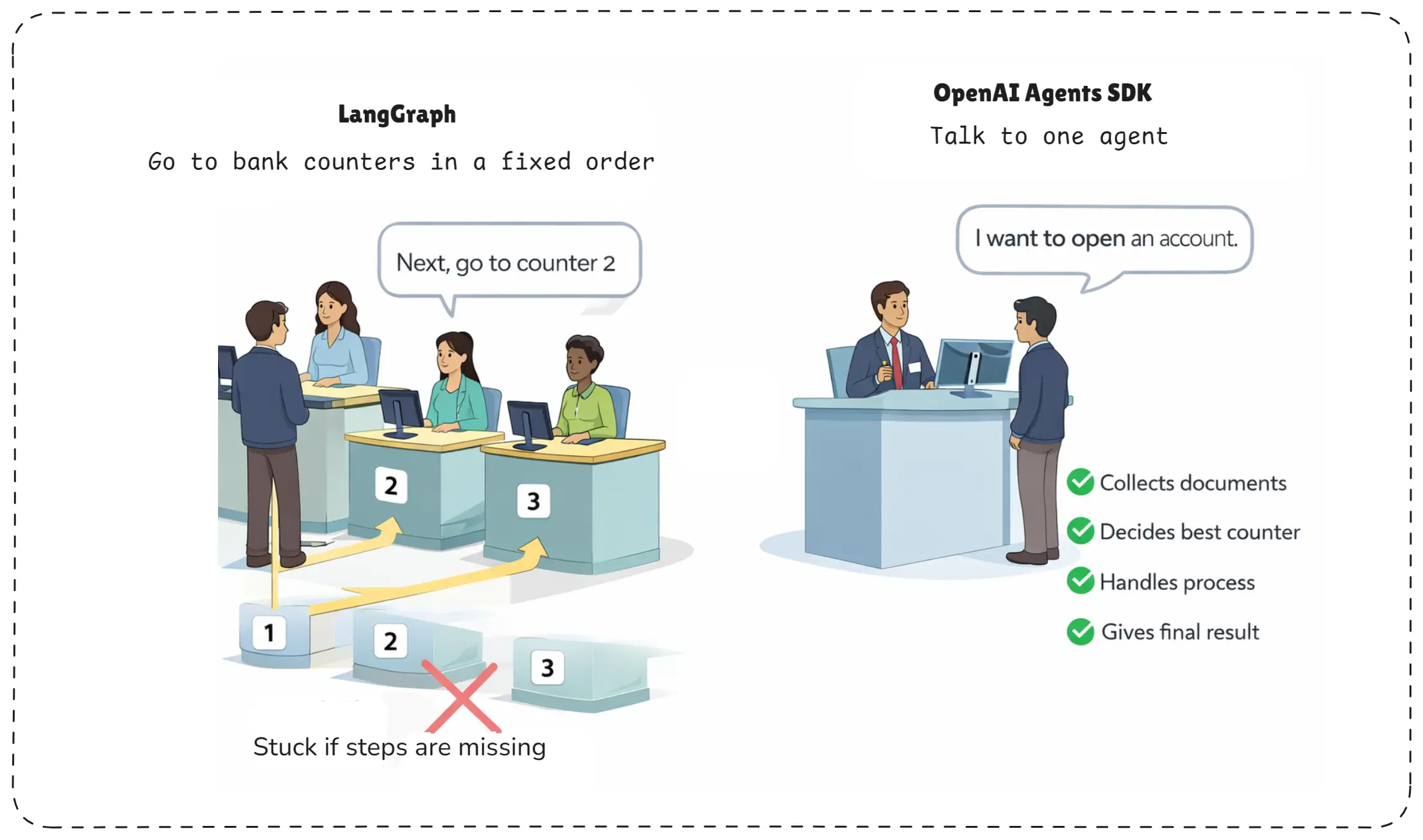
Bank Analogy for langgraph and openai agents sdk.webp
Now think of OpenAI Agents SDK like talking to a single knowledgeable bank employee.
You simply say, “I want to open an account.”
That person:
- Collects your documents
- Decides which counter to go to
- Handles the full process internally
- Gives you the final result
You never worry about the steps. The agent handles the workflow automatically.
4. Key Concepts for OpenAI Agents SDK
These concepts together make OpenAI Agents SDK powerful. Instead of manually controlling every step, you create capable agents, give them tools and boundaries, and let them handle the workflow intelligently. This is what makes Agents SDK ideal for autonomous, scalable, and real-world AI systems.
- Agents
- Running agents
- Tools
- Handoffs
- Streaming
- Human in the loop
- Threads & Tracing
- Guardrails
- Context management
- Session management
Understanding how these concepts connect helps you build more effective and reliable AI agents. For a deeper explanation, explore our complete guide on understanding AI agents.
1. Agents
In OpenAI Agents SDK, an agent is a smart AI worker that is created for a specific purpose. An agent is not just a chatbot that replies once. It can think step by step, decide what to do next, use tools when needed, and stop when the task is finished. You design the role of the agent, but the agent decides how to complete the task.
2. Running Agents
Running an agent means giving it a task and letting it work until completion. Once started, the agent manages its own flow. It decides when to call tools, when to ask for more information, and when the final answer is ready. You do not manually move it from step to step like in a workflow graph.
3. Tools
Tools are external abilities that an agent can use, such as calling APIs, searching the web, fetching data, or running calculations. In OpenAI Agents SDK, the agent decides when a tool is needed and how to use it. The developer only defines what tools exist and what they do.
4. Handoffs
Handoffs allow one agent to pass work to another agent. If an agent realizes that another agent is better suited for a task, it can transfer control. This makes it easy to build systems where multiple agents collaborate naturally, without hard-coding transitions.
5. Streaming
Streaming lets the agent send responses gradually instead of waiting for the full answer. This is useful when tasks take time, such as long reasoning or tool usage. Users can see progress in real time, which improves user experience and transparency.
6. Human in the Loop
Human in the loop means a person can step in during the agent’s execution. The agent can pause, ask for confirmation, or wait for approval before continuing. This is important for sensitive tasks like payments, approvals, or decision-making where human control is required.
7. Threads & Tracing
Threads keep track of conversations and actions over time. Tracing records what the agent did, which tools it used, and why it made certain decisions. This helps developers debug issues, understand agent behavior, and monitor performance in production.
8. Guardrails
Guardrails are safety rules that limit what an agent can do. They prevent harmful actions, unwanted outputs and inputs, or unsafe tool usage. Guardrails ensure the agent stays within allowed boundaries, even when it is acting autonomously.
9. Context Management
Context management controls what information the agent remembers and uses while working. Instead of sending everything every time, the agent keeps only relevant context. This improves performance, reduces confusion, and helps the agent stay focused on the task.
10. Session Management
Session management keeps each user’s interaction separate and consistent. It ensures that the agent remembers the correct state for each session and does not mix conversations between users. This is essential for multi-user and long-running applications.
5. OpenAI Agents SDK Environment Setup
Setting up the OpenAI Agents SDK in a Node.js environment is intentionally simple. The SDK is designed so you can start building real agents in minutes, not hours, without heavy configuration or complex frameworks.
To begin, make sure Node.js is installed on your system. A modern LTS version is recommended because the Agents SDK is TypeScript first and uses modern JavaScript features. You can quickly confirm installation by running node -v in your terminal.
Once Node.js is ready, create a new project folder for your agent. This keeps your agent code clean, isolated, and production-ready from day one.
mkdir openai-agents-sdk
cd openai-agents-sdk
npm init -yNow install the OpenAI Agents SDK along with zod, which is used internally for schema validation and guardrails.
npm install @openai/agents zod@3This single installation gives you everything needed to build agents, handle tool execution, manage handoffs, stream responses, and trace agent behavior.
Next, configure your OpenAI API key. The Agents SDK automatically reads the key from the environment, so you should never hard-code it in your source code.
Create a .env file in the root of your project and add your API key.
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-your-api-keyTo load environment variables automatically, install the dotenv package.
npm install dotenvThen import it at the top of your main file so the API key is available when your agent runs.
import"dotenv/config";With the environment ready, you can now create your first agent. Create a file such as index.ts (or index.js if you prefer JavaScript).
import "dotenv/config";
import { Agent, run } from '@openai/agents';
const agent = new Agent({
name: 'Assistant',
instructions: 'You are a helpful assistant',
});
const result = await run(
agent,
'Write a program for two sum in Java programming.',
);
console.log(result.finalOutput);When you run this file, the SDK automatically handles the entire agent loop for you. It sends the prompt to the model, manages reasoning, and returns the final response without you writing any orchestration logic.
node index.jsYou should see an output similar to two sum, confirming that your environment is correctly set up and the agent is working.
What makes this setup powerful is that nothing extra is required. There is no manual loop, no explicit tool routing, and no workflow wiring. The OpenAI Agents SDK handles execution, decision-making, and completion internally, giving you a clean and predictable developer experience.
At this stage, your Node.js environment is fully ready for building text agents, voice agents, tool-using agents, and multi-agent systems. From here, you can easily add tools, enable streaming, introduce guardrails, or connect multiple agents together using handoffs.
This simple setup is the foundation for everything you’ll build next with the OpenAI Agents SDK.
Conclusion
In this article, we clearly understood what the OpenAI Agents SDK is, why it exists, and how it solves the biggest problem in agent development: manual workflow control. Unlike procedural systems where developers must define every step, the Agents SDK allows agents to think, decide, and act on their own while still remaining safe, observable, and production-ready.
We explored how agents work internally, how tools, handoffs, guardrails, streaming, and tracing come together, and how setting up an agent in Node.js takes only a few minutes. Most importantly, we learned when and why OpenAI Agents SDK is a better choice than LangGraph, especially for autonomous and real-world applications.
The OpenAI Agents SDK represents a shift toward simpler, higher-level AI agent development. Instead of manually orchestrating workflows, developers can focus on intent, tools, and safety, while the SDK manages execution.
It is ideal when:
- You want fast development
- You trust autonomous decisions
- You need built-in streaming, tracing, and guardrails
OpenAI Agents SDK is not about control first it’s about speed, simplicity, and scale.
For teams building modern AI applications, it offers a powerful way to move from experiments to real, production-ready AI agents.
In the next phase, we’ll move from concepts to hands-on agent building. We’ll create real agents using OpenAI Agents SDK, design specialized agents, connect multiple agents together, and build fully autonomous workflows step by step. This is where agentic AI truly comes to life.
If you’re serious about building modern, scalable, and production-grade AI agents, the journey starts here and the real building begins next.
Happy agent building with OpenAI Agents SDK!